CCPC (Tinidazole Capsules) – Trichomoniasis | HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Tinidazole Capsules/CCPC
- Indications: Trichomoniasis
- Dosage Form: Capsules
- Specification: 50 mg × 8
Tinidazole Capsules Application Scope
Tinidazole Capsules are an antiprotozoal and antibacterial medication. They treat infections caused by specific parasites and bacteria. This drug belongs to the nitroimidazole class.
Indications
Tinidazole Capsules treat trichomoniasis caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. They also address giardiasis from Giardia duodenalis. For amebiasis due to Entamoeba histolytica, they cover dysentery and liver abscess—but not asymptomatic cysts.
In non-pregnant women, they manage bacterial vaginosis, excluding other causes. They help eradicate Helicobacter pylori in duodenal ulcers when combined with antibiotics and acid suppressants. They combat anaerobic bacterial infections like peritonitis, abscesses, endometritis, septicemia, wound infections, skin issues, pneumonia, lung abscess, empyema, and gingivitis.
They prevent postoperative anaerobic infections after colon, gastrointestinal, or urogenital surgeries.
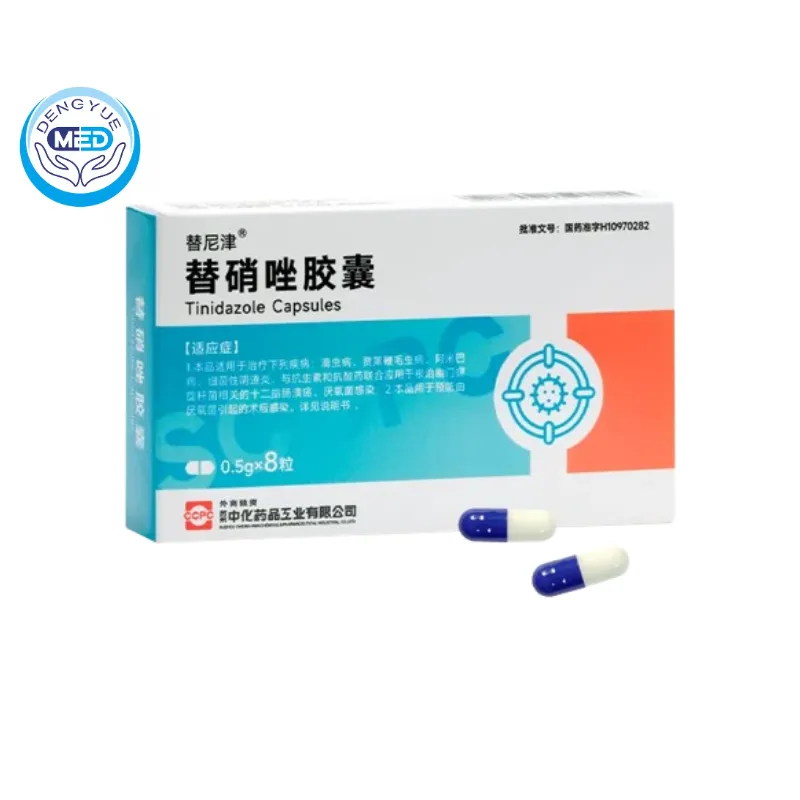
Tinidazole Capsules Characteristics
-
Ingredients: The main ingredient is tinidazole. Chemical name: 2-methyl-1-[2-(ethylsulfonyl)ethyl]-5-nitro-1H-imidazole. Molecular formula: C₈H₁₃N₃O₄S. Molecular weight: 247.28. The content of tinidazole should be 90.0%-110.0% of the labeled amount.
-
Properties: Capsule, with contents being slightly yellow powder or granules.
-
Packaging Specification: 0.5g8 capsules or 0.5g10 capsules per box.
-
Storage: Store in a shaded, sealed container.
-
Expiry Date: 24 months.
-
Executive Standard: Complies with national drug standards for tinidazole capsules.
-
Approval Number: National Medical Products Administration Approval No. H10970282 (国药准字H10970282).
-
Date of Revision: October 1, 2010; December 9, 2013.
-
Manufacturer: Suzhou Zhonghua Pharmaceutical Industry Co., Ltd.
Guidelines for the Use of Tinidazole Capsules
-
Dosage and Administration:
-
Recommended Dose: Adults generally take 2 g once for trichomoniasis and giardiasis; children over 3 years take 50 mg/kg once (max 2 g). Amebiasis is treated with 2 g daily for 3–5 days in adults and 50 mg/kg daily in children. Bacterial vaginosis uses either a short 2-day (2 g/day) or 5-day (1 g/day) regimen. H. pylori therapy is 500 mg twice daily for 7 days with omeprazole and clarithromycin. Anaerobic infections start with 2 g then continue with 1 g/day or 500 mg twice daily for several days, and surgical prophylaxis uses a single 2 g pre-op dose.
-
Administration: Oral administration. It is recommended to take after meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Food does not affect bioavailability.
-
Missed Dose: Missing a dose or not completing the course may reduce efficacy and lead to drug resistance; adhere strictly to the prescribed regimen. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it’s almost time for the next dose, then skip and resume normal schedule.
-
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Common Adverse Reactions: Gastrointestinal (metallic/bitter taste 3.7%-6.3%, nausea 3.2%-4.5%, anorexia 1.5%-2.5%, indigestion/cramps/epigastric discomfort 1.4%-1.8%, vomiting 0.9%-1.5%, constipation 0.4%-1.4%); central nervous system (weakness/fatigue/malaise 1.1%-2.1%, dizziness 0.5%-1.1%); other (headache 0.7%-1.3%, skin itching, rash). Overall incidence: 11.0% for single dose, 13.8% for multi-day dosing.
-
Serious Adverse Reactions: Convulsions, peripheral neuropathy (numbness, paresthesia), hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme), candidal overgrowth, abnormal liver function (elevated transaminases), hematologic abnormalities (leukopenia/neutropenia), psychiatric symptoms (depression, confusion), disulfiram-like reactions, dark urine, epilepsy seizures at high doses.
-
-
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to tinidazole or pyrrole drugs; patients with organic central nervous system diseases; history of blood disorders or cachexia; first trimester of pregnancy; lactating women (suspend breastfeeding during treatment and for 3 days after).
-
Precautions:
- Carcinogenic/mutagenic potential: Animal studies show carcinogenic and mutagenic effects, but human data is lacking. Discontinue if central nervous system adverse reactions occur. May interfere with lab tests (e.g., alanine aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides, making values appear zero). Avoid alcohol-containing beverages during treatment as it may cause acetaldehyde accumulation, leading to disulfiram-like reactions (abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, flushing). In hepatic impairment, metabolism slows, requiring dose reduction and blood concentration monitoring. In candida infections, symptoms may worsen, requiring antifungal treatment. For vaginal trichomoniasis, treat sexual partners simultaneously. Use in children limited to those over 3 years for specific indications. Elderly: Monitor due to potential hepatic changes. Pregnancy: Avoid in first trimester; use later only if clearly indicated. Lactation: Avoid or suspend breastfeeding for 3 days post-treatment. May decrease drug levels in patients with gastric tubes; hemodialysis clears the drug, no dose adjustment needed.
Tinidazole Capsules Interactions
- Enhances the effect of warfarin and other oral anticoagulants (prolongs prothrombin time; adjust dose during treatment and 8 days after). With alcohol/disulfiram: Avoid, may cause abdominal pain, nausea, etc. With lithium: May increase lithium levels; monitor serum lithium and creatinine. With phenytoin/fosphenytoin: May prolong phenytoin half-life. With cyclosporine/tacrolimus: May increase levels; monitor for toxicity. With fluorouracil: Reduces clearance; monitor for toxicity. CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, rifampin): Accelerate elimination, reduce plasma levels. CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine, ketoconazole): Prolong half-life, increase concentration. Cholestyramine: Reduces bioavailability; administer separately. Oxytetracycline: May antagonize effect on trichomonas. Interferes with lab tests (AST, ALT, LDH, triglycerides, cholesterol, glucose). With enzyme inducers (e.g., phenobarbital): Speeds metabolism, lowers blood levels, slows phenytoin excretion. With enzyme inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine): Slows metabolism and excretion, prolongs half-life; adjust dose based on blood levels.
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from DengYue Medicine.
- This content is for reference only. Prescription drugs must be used under a doctor’s guidance and purchased from authorized sources.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.