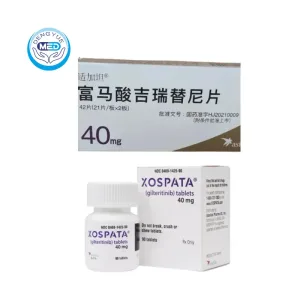
Xospata (Gilteritinib) – AML | HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Gilteritinib / Xospata®
- Indications: AML
- Dosage Form: Tablet
- Specification: 40 mg × 84 tablets/box
Gilteritinib Application Scope
Xospata is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who have a FLT3 mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test. It is an oral targeted therapy designed to selectively inhibit FLT3, a driver mutation associated with poor prognosis in AML, thereby providing an important treatment option for patients who have limited therapeutic alternatives.
Gilteritinib Characteristics
-
Ingredients: Active ingredient: Gilteritinib fumarate
-
Properties: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting FLT3 and AXL
-
Packaging Specification: 40 mg film-coated tablets, blister packs
-
Storage: Store at 20–25°C (68–77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F)
-
Expiry Date: As indicated on the package (typically 24–36 months from manufacture)
-
Executive Standard: International pharmaceutical quality standard (ICH, GMP compliance)
-
Approval Number: Refer to local regulatory authority approval code (e.g., FDA, EMA, NMPA)
-
Date of Revision: As per the latest prescribing information update
-
Manufacturer: Astellas Pharma Inc.
Guidelines for the Use of Xospata
-
Dosage and Administration:
-
Recommended Dose: 120 mg orally once daily
-
Administration: Take at the same time each day, with or without food. Swallow tablets whole.
-
Missed Dose: If a dose is missed or vomited, take the next scheduled dose at the regular time. Do not double-dose.
-
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Common Adverse Reactions:
-
Fatigue
-
Nausea
-
Diarrhea
-
Constipation
-
Elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST)
-
Muscle/joint pain
-
Rash
-
Fever
-
-
Serious Adverse Reactions:
-
Differentiation syndrome
-
QT interval prolongation
-
Pancreatitis
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)
-
-
-
Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity to Gilteritinib or excipients
-
Precautions:
-
Monitor ECG and electrolytes for QT prolongation.
-
Assess for differentiation syndrome and initiate corticosteroids promptly if suspected.
-
Monitor liver function, pancreatic enzymes, and blood counts.
-
Use caution in patients with severe renal or hepatic impairment.
-
Gilteritinib Interactions
-
CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin): May increase Gilteritinib exposure → risk of toxicity
-
CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, St. John’s Wort): May decrease Gilteritinib exposure → reduced efficacy
-
QT-prolonging drugs (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol, fluoroquinolones): Increased risk of cardiac arrhythmia
-
P-gp and BCRP substrates: Potential interactions; monitor closely
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from DengYue Medicine.
- This content is for reference only. Prescription drugs must be used under a doctor’s guidance and purchased from authorized sources.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.