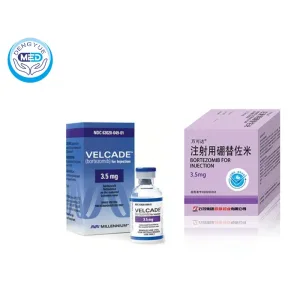
Velcade (Bortezomib) – Multiple Myeloma | HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Bortezomib/Velcade
- Indications: Multiple myeloma, relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma
- Dosage Form: Lyophilized powder for injection
- Specification: 3.5 mg × 1 vial
Bortezomib Application Scope
-
Bortezomib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with multiple myeloma (MM). Also approved for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
-
(In some regions) used for the re-treatment of multiple myeloma patients.
Bortezomib Characteristics
-
Ingredients: Bortezomib
-
Properties: A white to off-white cake or powder for reconstitution into a sterile solution
-
Packaging Specification: Single-dose vials containing 3.5 mg of bortezomib as a sterile lyophilized powder
-
Storage: Store in the original package at 25°C (77°F). Excursions are permitted between 15-30°C (59-86°F)
-
Expiry Date: As stated on the vial and outer packaging
-
Executive Standard: Complies with the specifications of the current approved product labeling
-
Approval Number: Specific to each country; see local product labeling
-
Date of Revision: For the latest version, check the official package insert
-
Manufacturer: Pfizer (Velcade)
Guidelines for the Use of Bortezomib
-
Dosage and Administration:
-
Recommended Dose:
-
The standard starting dose for many regimens: 1.3 mg/m² per dose.
-
Cycle scheduling depends on the treatment protocol (e.g., on days 1, 4, 8, and 11 in a 21-day cycle for some myeloma regimens).
-
-
Administration:
-
Intravenous (IV): Typically 3–5 second bolus injection.
-
Subcutaneous (SC): Alternative route; some regimens prefer SC because of lower neuropathy risk.
-
Reconstitution: e.g., for 3.5 mg vial, add 3.5 mL of 0.9% NaCl to make 1 mg/mL (for some Velcade formulations)
-
-
Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, the re-treatment or “catch-up” depends on the specific cycle schedule.
-
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Common Adverse Reactions:
Based on clinical studies/prescribing information: Nausea
-
Diarrhea
-
Thrombocytopenia
-
Neutropenia
-
Peripheral neuropathy
-
Fatigue
-
Neuralgia
-
Anemia
-
Leukopenia
-
Constipation
-
Vomiting
-
Lymphopenia
-
Rash
-
Fever (pyrexia)
-
Anorexia
-
-
Serious Adverse Reactions:
-
Peripheral neuropathy, including severe sensory and motor neuropathy.
-
Cardiovascular: heart failure, pulmonary edema, QT-interval prolongation (isolated cases)
-
Pulmonary toxicity: acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis.
-
Hematologic toxicity: cyclic thrombocytopenia / neutropenia.
-
Thrombotic microangiopathy (per more recent label updates)
-
Tumor lysis syndrome in patients with high tumor burden.
-
Embryo-fetal toxicity: potential fetal harm; advise females of reproductive potential to avoid pregnancy.
-
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) (in some reported cases)
-
-
-
Contraindications:
-
Hypersensitivity to bortezomib, boron, or mannitol (some formulations contain mannitol).
-
Intrathecal administration (into the spine) is absolutely contraindicated—fatal events have occurred.
-
-
Precautions:
-
Patients with pre-existing peripheral neuropathy should be monitored closely; dose modification or discontinuation may be required if neuropathy worsens.
-
Cardiac monitoring: patients with heart disease or risk factors may need close monitoring (risk of heart failure, fluid overload).
-
Pulmonary symptoms: new or worsening dyspnea/infiltrates → interrupt therapy and evaluate.
-
Hematologic parameters: frequent CBC monitoring because of thrombocytopenia/neutropenia.
-
Hepatic impairment: In moderate/severe liver dysfunction, dose adjustment may be needed.
-
Pregnancy: may cause fetal harm; counsel women of childbearing potential.
-
Hypotension: caution in patients with dehydration, those on antihypertensives, history of syncope.
-
Tumor lysis: monitor high-burden disease for tumor lysis syndrome.
-
Bortezomib Interactions
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) can increase bortezomib exposure.
- PMCCYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) can decrease bortezomib exposure; use with caution/avoid.
- PMC: Because bortezomib is metabolized by multiple CYPs, other drugs affecting CYP pathways may interact.
- Proper handling: Cytotoxic drug handling procedures should be followed during preparation/administration.
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from DengYue Medicine.
- This content is for reference only. Prescription drugs must be used under a doctor’s guidance and purchased from authorized sources.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.