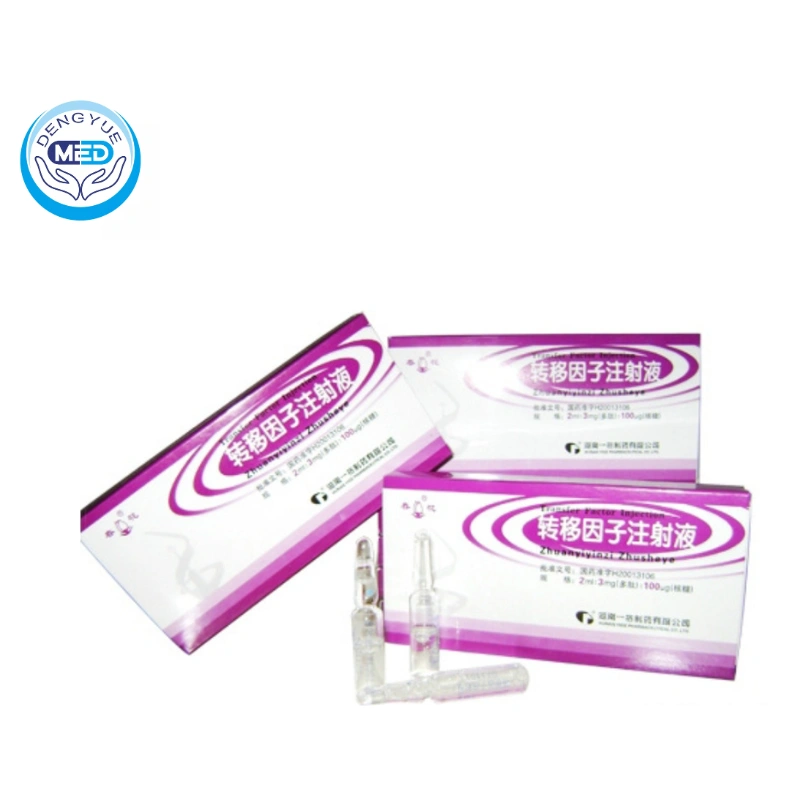
Transfer Factor Injection | Other Tumors | HK DengYueMed
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Transfer Factor Injection /Hunan Yige Pharmaceutical
- Indications: Soft Tissue Sarcoma, Other Tumors
- Dosage Form: White loose solid
- Specification: 2 ml: 3 mg (peptide): 100 mcg (ribose)
Transfer Factor Injection Application Scope
Transfer Factor Injection is used primarily to modulate the immune system, often for individuals with weakened immunity or conditions requiring immune enhancement. Transfer factors are small molecules that carry immune information from one organism to another, and are used to help boost immune function and improve resistance to infections. They are derived from bovine colostrum or human sources, and have been studied for various immunologic applications.
- Primary Uses:
- Used in immune deficiency conditions such as chronic infections (e.g., chronic viral infections, bacterial infections).
- Adjunctive therapy in autoimmune diseases (as part of immunomodulation).
- Cancer immunotherapy: To enhance immune response against tumors.
- Potentially beneficial in conditions where the immune system is weakened, such as post-surgery or chemotherapy recovery.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Transfer factor molecules work by transferring specific immune information (antigens or immune signals) to immune cells, enhancing the body’s response to infections or immune challenges.
- They stimulate T-cell and B-cell activity, promoting the activation of macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells, which helps in the identification and destruction of pathogens or abnormal cells.
Transfer Factor Injection – Characteristics
- Ingredients:
- Active Ingredient: Transfer factors derived from colostrum (usually bovine or human) or from white blood cells (leukocytes).
- Inactive Ingredients: May include saline, phosphate buffers, preservatives, and stabilizers depending on the formulation.
- Properties:
- Immunomodulatory: Helps to modulate and enhance the immune system.
- Transfer factor injection is typically a clear, sterile solution administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
- Specification: 2 ml: 3 mg (peptide): 100 mcg (ribose)
- Packaging Specification: 2ml:3mg:100μg*10 sticks
- Storage: Keep airtight and in a cool, dark place.
- Expiry Date: 18months
- Executive Standard: State Drug Administration National Drug Standard WS1-XG-038-2000
- Approval Number: National Drug Code H20013106
- Date of Revision: Indicated on the packaging to show when the product was last updated or reviewed.
- Manufacturer: Hunan Yige Pharmaceutical
Guidelines For The Use Of Transfer Factor Injection
- Dosage and Administration:
- Standard Adult Dose:
- Typically 250 mcg to 1 mg once daily or as directed by the healthcare provider.
- The injection may be administered either subcutaneously (SC) or intramuscularly (IM), depending on the formulation.
- Pediatric Dose:
- Dosing is usually lower and determined by the child’s weight and specific condition, often ranging from 125 mcg to 500 mcg.
- Duration:
- The duration of treatment depends on the condition being treated. A typical course may last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
- Route of Administration:
- Most commonly administered via subcutaneous injection or intramuscular injection.
- Standard Adult Dose:
- Adverse Reactions:
- Common:
- Injection site reactions (pain, redness, swelling).
- Mild fever or chills.
- Fatigue or headache.
- Serious:
- Severe allergic reactions: Rare, but symptoms may include rash, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face or throat.
- Immunologic responses: In some cases, an overstimulated immune response can lead to autoimmune flare-ups or exacerbation of pre-existing immune disorders.
- Local tissue reactions at the injection site.
- Common:
Medication Limitations
- Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity: Contraindicated in patients with known allergies to transfer factors or any of the excipients in the formulation.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Use with caution in individuals with autoimmune conditions unless specifically indicated, as transfer factors could potentially exacerbate the condition.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Limited data on the safety of transfer factor injections during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is best to avoid use unless recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Precautions:
- Immune System Disorders: Patients with compromised immune systems (e.g., HIV/AIDS, organ transplant recipients) should be carefully monitored.
- Allergic Reactions: As with any immune-boosting product, be cautious of potential allergic reactions. A test dose may be recommended for individuals with a history of hypersensitivity reactions.
- Chronic Infections: Caution is advised in individuals with chronic infections or cancer as the immune response may be unpredictable.
Transfer Factor Injection Interactions
- Drug Interactions:
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: Drugs like corticosteroids, chemotherapy agents, or immunosuppressants may reduce the efficacy of transfer factor injections.
- Vaccines: Caution is needed when administering live vaccines during transfer factor treatment, as the immune response may be altered.
- Other Immune Modulators: Combining transfer factor injections with other immune-modulating drugs (e.g., interferons, monoclonal antibodies) may lead to an excessive immune response.
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from HongKong DengYue Medicine. It is only for internal discussion among medical staff and does not serve as a basis for medication. For specific medication guidelines, please consult the attending physician.
Contact Us





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.