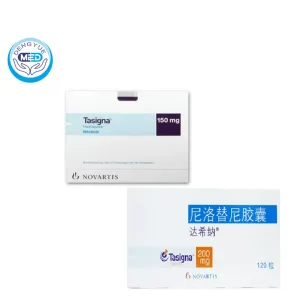
Tasigna (Nilotinib) – CML | HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Nilotinib/Tasigna
- Indications: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Ph+ CML
- Dosage Form: Capsule/Hard gelatin capsule
- Specification: 150 mg/200 mg × 120 capsules
Tasigna Application Scope
-
Tasigna (nilotinib) is indicated for:
-
Adult and pediatric patients (≥ 1 year) with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (Ph+ CML-CP).
-
Adult patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase (CP) or accelerated phase (AP) who are resistant or intolerant to prior therapy, including imatinib.
-
Pediatric patients ≥ 1 year with Ph+ CML-CP resistant or intolerant to prior TKI therapy.
tasigna nilotinib
-
Tasigna Characteristics
-
Ingredients: Nilotinib
-
Properties: Oral formulation
-
Packaging Specification: Varies by country and strength (e.g., 50 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg hard capsules)
-
Storage: Store in a dry place, below 30 °C (86 °F); protect from heat, moisture and light
-
Expiry Date: Use the expiration date printed on the packaging
-
Executive Standard: Depends on local regulatory standards
-
Approval Number: Specific to each country; see local product labeling
-
Date of Revision: For the latest version, check the official package insert
-
Manufacturer: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
Guidelines for the Use of Tasigna
-
Dosage and Administration:
-
Recommended Dose:
-
Newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP (adult, first-line): 300 mg twice daily (i.e., 300 mg × 2).
-
Resistant/intolerant Ph+ CML (CP or AP): 400 mg twice daily (i.e., 800 mg/day).
-
Pediatric dosing: Weight/BSA-based; see local pediatric dosing in package insert.
-
-
Administration:
-
Take on an empty stomach: No food for at least 2 hours before the dose and no food for at least 1 hour after the dose.
-
Swallow capsules whole with water; do not chew, crush, or open.
-
Space doses approximately 12 hours apart.
-
Perform ECG monitoring (baseline, ~7 days after start, after dose changes, and periodically thereafter) and monitor electrolytes (potassium, magnesium) prior to and during therapy.
-
-
Missed Dose:
-
If less than ~6 hours late, take dose as soon as possible (observing empty stomach rule).
-
If more than ~6 hours late, skip the missed dose; take the next dose at scheduled time. Do not double up.
-
Refer to local label for more precise guidance.
-
-
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Common Adverse Reactions:
-
Rash, pruritus (itching).
-
Headache, fatigue, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, and vomiting.
-
Myalgia, arthralgia, and back pain.
-
Hematologic: Thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia.
-
Elevated bilirubin or liver enzymes (AST, ALT).
-
Elevated pancreatic enzymes (lipase, amylase).
-
Hyperglycemia (blood glucose increase).
-
-
Serious Adverse Reactions:
-
QT interval prolongation, torsades de pointes, and sudden death—a boxed warning in many labels.
-
Vascular events: Peripheral arterial occlusive disease, ischemic heart disease, and cerebrovascular events.
-
Hepatotoxicity, severe liver injury.
-
Pancreatitis (abdominal pain with elevated lipase).
-
Hemorrhage (bleeding).
-
Tumor lysis syndrome (rare).
-
-
-
Contraindications:
-
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia (unless corrected).
-
Congenital long QT syndrome.
-
Hypersensitivity to nilotinib or any component of the formulation.
-
-
Precautions:
-
Monitor ECG/QTc and correct electrolyte abnormalities before and during treatment.
-
Evaluate and manage cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and smoking) because of risk of arterial events.
-
Hepatic impairment: caution; may require dose reduction and closer QT monitoring.
-
Pancreatic enzyme monitoring; interrupt dose if pancreatitis suspected.
-
Monitor for signs of bleeding.
-
In pediatric patients, monitor growth and development.
-
Pregnancy/fetal risk: may cause fetal harm; use effective contraception.
-
Caution in patients with prior gastric surgery (e.g., gastrectomy) may affect absorption.
-
Tasigna Interactions
-
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin): may increase nilotinib levels → increased QT risk.
-
Strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin): may reduce nilotinib levels → reduced efficacy.
-
Drugs that prolong QT interval: additive risk → avoid concomitant use.
-
Grapefruit/grapefruit juice: avoid (affects CYP3A4 and nilotinib absorption)
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from DengYue Medicine.
- This content is for reference only. Prescription drugs must be used under a doctor’s guidance and purchased from authorized sources.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.