Pretomanid|Tuberculosis (TB)|HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Pretomanid/Dovprela
- Indications: Tuberculosis
- Dosage Form: Film-coated tablets
- Specification: 200 mg
Pretomanid Application Scope
Pretomanid drug is an antimycobacterial agent indicated for use as part of a combination regimen with bedaquiline and linezolid for the treatment of adults with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) that is resistant to isoniazid, rifamycins, a fluoroquinolone, and a second-line injectable antibacterial drug, or for adults with pulmonary TB resistant to isoniazid and rifampin who are treatment-intolerant or nonresponsive to standard therapy.
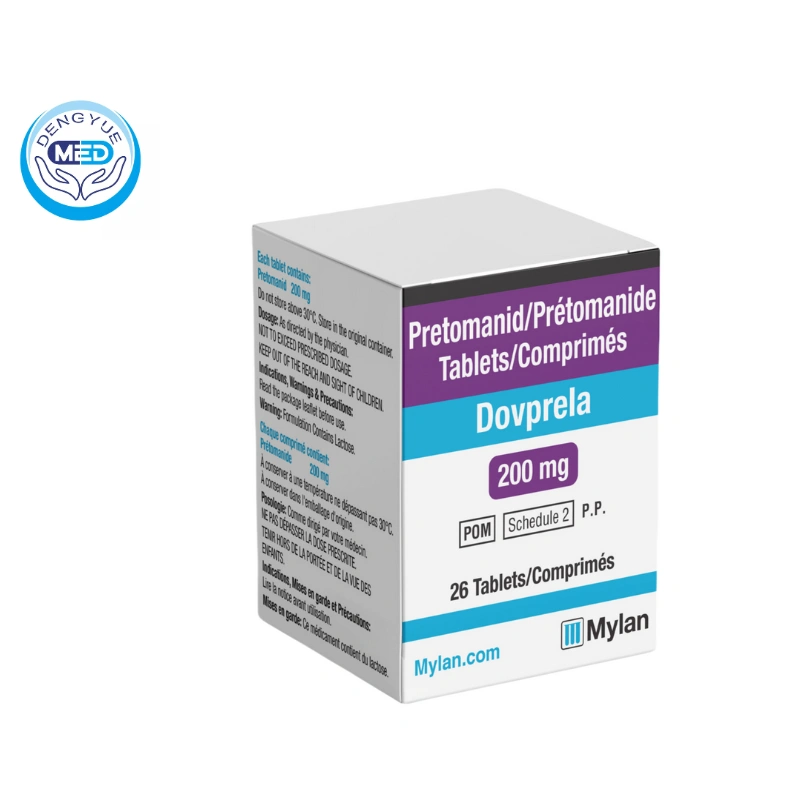
Pretomanid Characteristics
- Ingredients: Each tablet contains 200 mg of pretomanid.
- Properties: It is a nitroimidazooxazine antimycobacterial drug that inhibits mycolic acid biosynthesis, thereby blocking cell wall production in actively replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Under anaerobic conditions, it acts as a respiratory poison following nitric oxide release.
- Specification: Film-coated tablets containing 200 mg of pretomanid tablets.
- Packaging Specification: Typically supplied in bottles containing 26 tablets.
- Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- Expiry Date: Refer to the packaging for the specific expiration date.
- Executive Standard: Manufactured in compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP).
- Approval Number: NDA 212862.
- Date of Revision: November 2024.
- Manufacturer: Viatris Specialty LLC.
Guidelines for the Use of Pretomanid Drug
-
Dosage and Administration: The recommended dosage is 200 mg (one tablet) of pretomanid taken orally once daily for 26 weeks. It must be administered in combination with bedaquiline and linezolid. Bedaquiline is administered at 400 mg once daily for the first 2 weeks, followed by 200 mg three times per week (with at least 48 hours between doses) for a total of 26 weeks. Linezolid is initiated at 1,200 mg daily, with dose adjustments as necessary based on tolerability. All three medications should be taken with food.
-
Adverse Reactions: Common adverse reactions (≥10% incidence) include peripheral neuropathy, acne, anemia, nausea, vomiting, headache, increased transaminases, dyspepsia, rash, decreased appetite, and pruritus. Serious adverse reactions may include myelosuppression, hepatotoxicity, and lactic acidosis.
-
Contraindications: There are no specific contraindications listed for pretomanid drug. However, contraindications related to bedaquiline and linezolid should be considered when used in combination.
-
Precautions: Monitor for hepatotoxicity, myelosuppression, peripheral and optic neuropathy, and lactic acidosis. Caution is advised in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents during treatment.
Pretomanid Interactions
- Drug Interactions: Pretomanid tablets are metabolized primarily by CYP3A4. Co-administration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine) may decrease pretomanid plasma concentrations, reducing its efficacy; such combinations should be avoided. Pretomanid may increase the plasma concentrations of drugs that are substrates of OATP1B3; monitoring for adverse effects is recommended when co-administered. Additionally, concurrent use with alcohol or hepatotoxic agents may enhance the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from HongKong DengYue Medicine. It is only for internal discussion among medical staff and does not serve as a basis for medication. For specific medication guidelines, please consult the attending physician.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.