Is Chronic Hepatitis C Curable? Discover 6 Vital Facts

Table of Contents
Introduction
Millions of Americans are infected with hepatitis C and don’t even know it. Hepatitis C has been called a “silent epidemic” because people can be infected for decades and not even know it.
In fact, 70% or more of those infected show no signs or symptoms. Those who do have signs or symptoms usually experience fever, fatigue, or nausea, which can indicate almost any problem.
If you are between the ages of 54 and 74, you are five times more likely to have hepatitis C than someone older or younger.
What Is A Chronic Hep C Infection?
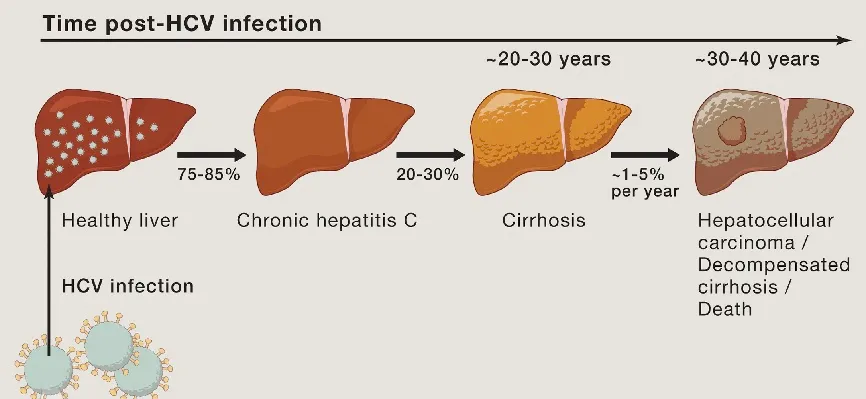
Chronic Hepatitis C is a long-lasting liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). While many experience no symptoms initially, around 80% of acute infections become chronic.
Over decades, untreated cases often lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Modern antiviral therapy aims for sustained virologic response (SVR)—undetectable virus 12 weeks post-treatment—which significantly lowers fibrosis progression, liver failure, and cancer risk.
NS5A Inhibitors: The Game-Changers
NS5A is a crucial viral protein involved in HCV replication and assembly. By blocking NS5A, inhibitors like Ravidasvir and Emitasvir disrupt the virus lifecycle, often achieving cure rates above 95% when combined with other antivirals like sofosbuvir
Chronic Hepatitis C Symptoms
Most people with chronic Hepatitis C don’t feel sick and often don’t realize they’re infected—symptoms may not show for 20 years or more.
When symptoms develop, they tend to be mild, vague, and non‑specific—making diagnosis challenging without blood tests.
Here are some common symptoms of Chronic Hepatitis C:
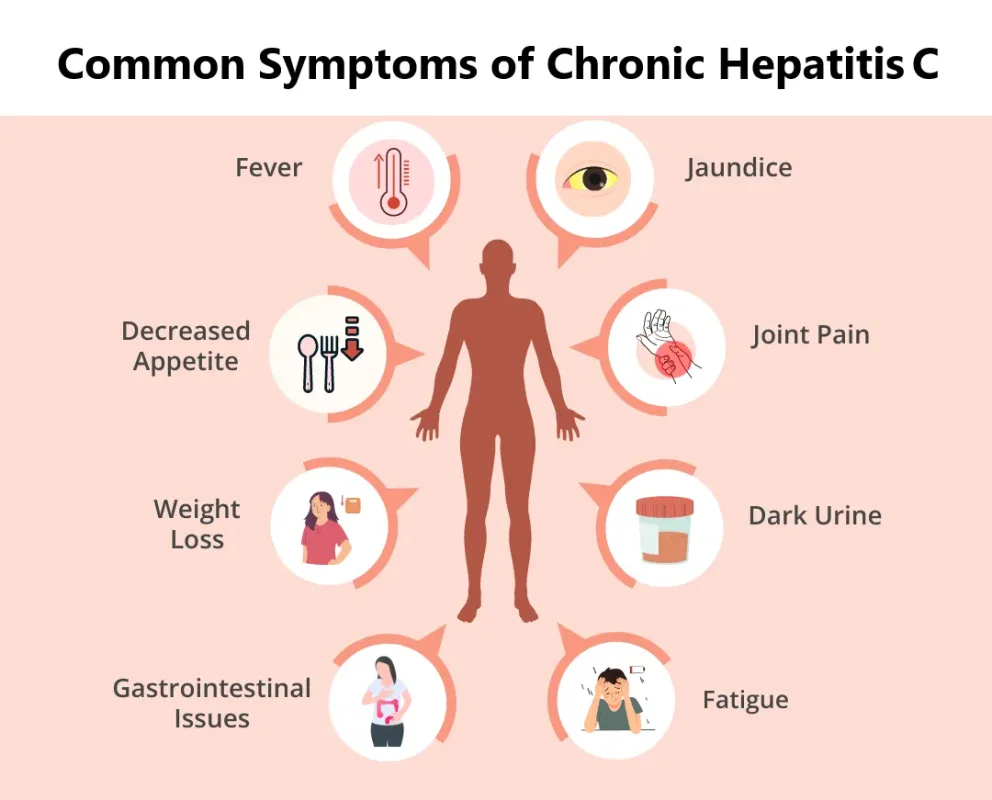
❗Fatigue and general malaise
❗Loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal discomfort
❗Joint and muscle aches (“flu‑like” symptoms)
❗Dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice
❗Itchy skin (pruritus)
❗Brain fog, mood disturbances
Signs of advanced liver disease. In cirrhosis, look for:
❗Ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen)
❗Peripheral edema (leg swelling)
❗Spider angiomas, palmar redness
❗Easy bruising/bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding
❗Hepatic encephalopathy: confusion, sleep issues, slurred speech
Chronic Hepatitis C Causes
Chronic Hep C develops when the hepatitis C virus (HCV) remains in the body for more than six months. The infection occurs only through blood-to-blood exposure, not via casual contact.
Major Transmission Routes
Sharing needles or injection equipment: The most common route—especially among people who inject drugs, with up to 90% infection rates among long-term users
Blood transfusions and organ transplants (pre-1992): Before rigorous screening, receiving blood or organs carried a significant risk
Unsterilized medical or dental instruments: Includes improperly disinfected needles, scalpels, and multi-use vials
Tattoos, piercings, body modification with non-sterile tools: Especially in unregulated settings like prisons or underground parlors
Less Common Routes
Mother-to-child (vertical transmission): Occurs in about 5% of cases during pregnancy or childbirth
Needlestick injuries in healthcare settings: Accidental puncture from HCV-positive needles carries a small but real risk (~1–2%)
Shared personal items: Razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers can pose infection risks if they carry blood .
Sexual transmission: Relatively rare, but higher risk with multiple partners, HIV co-infection, anal sex, or during menstruation
🛑 What Doesn’t Transmit HCV?
Avoid anxiety over casual interactions—HCV does not spread through:
- Hugging, kissing, or shaking hands
- Sharing food, drinks, dishes, or utensils
- Sneezing, coughing, or toilet seats
- Mosquito or insect bites
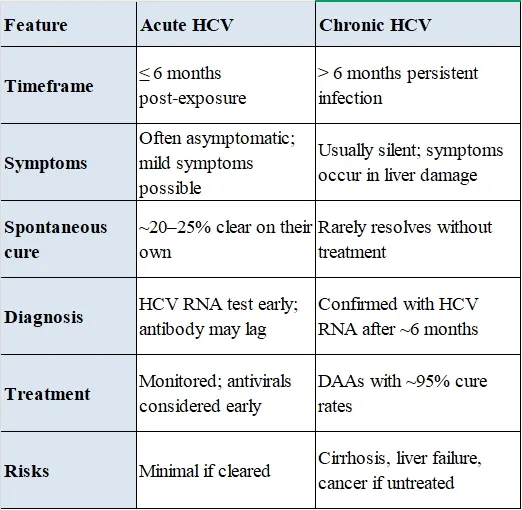
Acute vs. Chronic Hepatitis C
Here’s a clear comparison between Acute and Chronic Hepatitis C:
Is Chronic Hepatitis C Curable?
Yes — Chronic Hepatitis C is highly curable, thanks to modern antiviral medications.
Chronic hepatitis C is no longer a life sentence. The vast majority of cases are curable and early treatment can save lives.
While drug treatments can be expensive, they are transformative – offering a real pathway to eradicating the virus.
Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
When it comes to Chronic Hepatitis C medications, the following medicines cannot be ignored.

Ascletavir (Ravidasvir) is an investigational, pan-genotypic NS5A inhibitor developed by Pharco Pharmaceuticals and studied extensively in combination with sofosbuvir.
Most side effects were mild (e.g., fever, cough, headache). No drug-related serious events were reported, nor discontinuations.

Emitasvir is another orally active NS5A inhibitor under clinical development, notably in China.
Generally well tolerated. Adverse events were mild, and serious AEs weren’t tied to the drug.
Both drugs support once-daily dosing and ribavirin-free combinations—easier for patients and healthcare systems. Effective even in harder-to-treat groups (cirrhosis, HIV co-infection, genotype 3).
Conclusion
Ravidasvir and emitasvir represent the next wave of accessible, effective HCV therapies. For global health, especially in LMICs, their simplicity, safety, and affordability could be transformative.
As treatment data grows and more countries adopt approvals, these regimens may significantly advance towards the eradication of chronic Hepatitis C.
About DengYueMed—HK Drug Wholesale Distributor
As a legally compliant drug import and export company, DengYue is certified by the Pharmacy & Poisons Board of Hong Kong — you can verify our qualification on their official website.

Our efforts to improve the affordability of HCV treatment aim to ensure that more patients can benefit from this important medication.
HK DengYue provides detailed medicine information, transparent pricing, and responsive support to ensure a smooth and reliable buying experience.
Feel free to reach out anytime to discuss your needs or ask questions about the medicine. We welcome you to contact us for a consultation.
FQA about Chronic Hep C
What’s the Difference between Hep C And Chronic Hep C?
“Hep C” just means infection with the hepatitis C virus. If the infection persists past 6 months, it becomes chronic Hep C, which requires treatment to avoid serious liver complications.
How to Determine If Hep C Is Acute or Chronic?
Acute HCV is diagnosed by early RNA detection, ALT elevation, and evidence of recent antibody seroconversion within the first 6 months.
If HCV RNA persists beyond 6 months, with ongoing liver enzyme abnormalities and no seroconversion pattern, it’s chronic HCV.
Does Hep C Stay in Your Body Forever?
No — hepatitis C does not stay in your body forever.
How Do You Treat Chronic Hep C?
Chronic hepatitis C (HCV) is treated with direct‑acting antivirals (DAAs)—oral medications that target key viral proteins.