2026 Pharma Trends 丨 Which 11 Drugs Will Define the Future of Pharma?
As global demographic shifts, evolving disease landscapes, and rising expectations for treatment experience continue to reshape healthcare, the pharmaceutical industry is facing unprecedented opportunities and challenges.
As a critical bridge between pharmaceutical innovation and clinical practice, Hong Kong DengYue Medicine closely monitors therapies with the potential to redefine treatment paradigms and reshape market dynamics.
🤔 Which 11 drugs will define the future of pharma in 2026?
In this article, we focus on four key therapeutic areas—metabolic diseases, rare diseases, oncology and immunology, and drug delivery technologies —and provide an in-depth analysis of 11 high-potential drugs expected to deliver both transformative clinical value and significant market impact in 2026.
Segmented Analysis: How 4 Therapeutic Frontiers Are Being Redefined
Pharmaceutical innovation is unfolding with unprecedented breadth and depth.
Looking across Clarivate’s annual selection of Which 11 Drugs Will Define the Future of Pharma, four primary innovation battlegrounds emerge with remarkable clarity: metabolic disease, rare disease, oncology and immunology, and drug delivery technologies.
🌐 These domains do not exist in isolation; together, they form a coherent landscape of pharmaceutical innovation—each undergoing its own paradigm shift while simultaneously influencing and reinforcing the others.
✨ More importantly, the trajectories of these four battlegrounds reveal a shared underlying trend: a transition from single-point intervention to system-level modulation, from treating disease to optimizing the patient experience, and from isolated therapeutic advances to integrated innovation networks.
Following, we examine how these four battlegrounds are being redefined—and how these 11 drugs are acting as catalysts of transformation within their respective domains.
2026 Pharma Trend #1: Metabolic Therapies Move Beyond Weight Management
Metabolic disease therapeutics are standing at a pivotal inflection point.
❗ As the global prevalence of overweight and obesity continues to rise—with adult rates projected to exceed 50% by 2030—this field has shifted from a peripheral health concern to a central public health challenge.
🔻 Historically, treatment strategies focused narrowly on glycemic control or modest weight reduction. Today, that paradigm is being fundamentally rewritten.
The success of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists has not only validated the central role of hormonal pathways in metabolic regulation but also opened the door to multi-target, multi-organ therapeutic strategies.
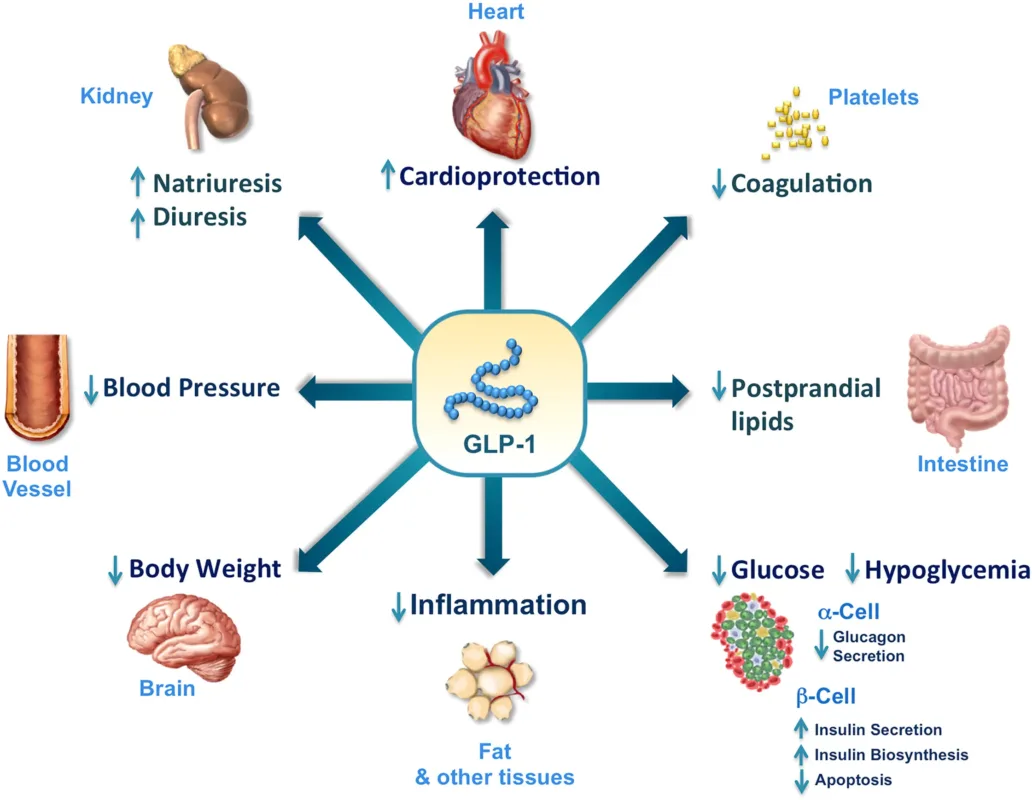
Metabolic therapy is now expanding beyond its traditional boundaries, extending into cardiovascular protection, renal preservation, neuroprotection, and even mental health.
A new era is emerging—one defined by the pursuit of system-wide metabolic homeostasis, rather than isolated symptom control.
👉 Against this backdrop, Eli Lilly’s orforglipron and retatrutide stand out as emblematic agents of this transformation.
- 1️⃣ Orforglipron
✨ Orforglipron, the first oral, non-peptide GLP-1 receptor agonist to advance into Phase III clinical trials, represents far more than an incremental formulation upgrade.
- It breaks through the long-standing bioavailability barriers that have confined GLP-1 therapies to injectable peptides.
- Through small-molecule design, orforglipron enables genuine dosing freedom—allowing once-daily administration without fasting requirements or timing constraints.
At its core, this innovation reflects a deep integration of medicinal chemistry and pharmacokinetic optimization.
Beyond patient convenience, the implications are systemic: simplified manufacturing, no cold-chain dependency, and scalability that makes global deployment—particularly in resource-limited settings—feasible.
In this sense, orforglipron may become a critical enabler of GLP-1 therapy democratization worldwide.
🔬 Beyond obesity and type 2 diabetes, its pipeline now includes obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension, reflecting a growing recognition that obesity is not a standalone condition but a multisystem metabolic disorder driven by insulin resistance.
Under this framework, success is no longer defined by the number on the scale alone, but by the reversal of downstream pathological cascades affecting cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic function.
- 2️⃣ Retatrutide
✨ By contrast, Retatrutide represents the apex of pharmacologic synergy.
Rather than merely combining the effects of GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor agonism, retatrutide employs a single, finely tuned molecule to synchronously activate three key metabolic pathways.
This coordinated mechanism enhances appetite suppression while simultaneously engaging the glucagon receptor as an “energy expenditure switch,” enabling bidirectional regulation of energy balance.
🔬 The Phase II data—showing an average 24.2% weight reduction at 48 weeks—has been widely described as “surgery-level efficacy.”
This comparison is not rhetorical: the magnitude of effect overlaps with outcomes seen in bariatric procedures such as gastric bypass, positioning retatrutide as a pharmacologic alternative to invasive metabolic interventions.
Retatrutide’s profound impact on hepatic fat reduction—up to 82% in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease—further underscores the disease-modifying potential of next-generation therapies.
✨ These findings suggest that future metabolic treatments may not only treat obesity-related complications but also actively interrupt the disease continuum from obesity to fatty liver, fibrosis, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma.
🔴 Taken together, orforglipron and retatrutide signal a decisive shift: metabolic medicine is moving beyond weight loss toward preventive, system-level metabolic reprogramming, redefining both the scope and ambition of therapy in this field.
2026 Pharma Trend #2: Rare Diseases Shift from Therapeutic Void to Precision and Durability
For decades, the rare disease space has remained under the shadow of neglect. Of the more than 7,000 known rare diseases worldwide, only around 500 currently have therapies approved by the FDA or EMA.
😖 Prolonged diagnostic delays—averaging up to five years—limited disease awareness, and highly fragmented patient populations have historically created formidable barriers to development and commercialization.
Yet this landscape is now undergoing a quiet but profound transformation. Advances in genomic sequencing, target discovery, and precision medicine have repositioned rare diseases from a therapeutic dead end into a frontier for validating breakthrough innovation models.
Importantly, rare disease R&D has expanded well beyond oncology, penetrating neurological, hematological, metabolic, and immune-mediated disorders.
✨ The core mission is evolving—from merely “offering a treatment option” to redefining diagnostic and therapeutic pathways at a disease-system level.
👉 Within this paradigm shift, BGB-16673, VOYXACT (sibeprenlimab), Exdensur (depemokimab), and tolebrutinib exemplify four distinct yet converging breakthrough strategies.
- 1️⃣ BGB-16673
BGB-16673, developed by BeiGene, represents the successful translation of targeted protein degradation into hematologic malignancies.
Rather than simply inhibiting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) activity, it harnesses the cell’s ubiquitin–proteasome system to selectively tag and eliminate the pathogenic BTK protein itself.
✨This approach is particularly powerful because it enables degradation of both wild-type BTK and mutant variants that render conventional BTK inhibitors ineffective—directly addressing one of the most persistent clinical challenges: acquired resistance.
The emergence of BGB-16673 may reshape treatment sequencing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, positioning protein degraders as preferred options following resistance to traditional BTK inhibition.
- 2️⃣ VOYXACT (sibeprenlimab)
VOYXACT (sibeprenlimab) illustrates the precision of true disease-causal intervention in IgA nephropathy.
👉 Instead of focusing on downstream manifestations such as proteinuria or hypertension, it targets the upstream driver—A Proliferation-Inducing Ligand (APRIL).
By inhibiting APRIL, VOYXACT reduces the production of galactose-deficient IgA1, thereby preventing formation of pathogenic immune complexes at the source of disease initiation.
VOYXACT advances IgA nephropathy from symptom management toward mechanism-based therapy, addressing disease progression at its biological root.
- 3️⃣ Exdensur (depemokimab)
Exdensur (depemokimab) pushes the concept of durability to its practical limit.
Through advanced antibody engineering, its half-life has been extended to support once-every-six-months subcutaneous dosing, while maintaining high-affinity IL-5 neutralization.
This ultra-long-acting profile carries transformative implications for chronic diseases requiring sustained suppression, redefining what long-term disease control can look like in real-world practice.
Exdensur’s semiannual dosing interval fundamentally reconfigures severe asthma care, transforming sustained clinical remission from an aspirational goal into a realistic outcome.
- 4️⃣ Tolebrutinib
Tolebrutinib overcomes one of the most formidable physiological barriers in drug development—the blood–brain barrier.
As a CNS-penetrant BTK inhibitor, it directly modulates immune activity within the brain and spinal cord by targeting B cells and microglia, the key drivers of chronic neuroinflammation associated with disability progression in multiple sclerosis.
This central mechanism distinguishes it from peripheral immunomodulators, which are largely unable to access this pathogenic compartment.
Tolebrutinib holds the potential to become the first disease-modifying therapy for non-relapsing secondary progressive multiple sclerosis—an area with profound unmet need and limited historical progress.
🔴 What unites these therapies is that they are not merely new products, but creators of new categories and new standards of care.
2026 Pharma Trend #3: Oncology and Immunology Shift from Target Inhibition to Protein Degradation and Pathway Synergy
Oncology and immunology have entered a complex post–immune checkpoint inhibitor era.
The success of PD-1/PD-L1 therapies conclusively demonstrated that the immune system can be mobilized to fight cancer—but it also exposed fundamental limitations.
🤔 A substantial proportion of patients fail to respond, and many who initially benefit eventually develop resistance.
At the same time, scientific understanding of tumor biology has deepened. Cancer is no longer viewed as the consequence of a single genetic mutation, but rather as a systems-level disease involving intersecting signaling pathways, tumor–microenvironment interactions, metabolic reprogramming, and immune evasion.
This recognition has catalyzed a new generation of therapeutic strategies—shifting from simply “blocking” oncogenic targets to eliminating disease-driving proteins, coordinating multi-pathway modulation, and re-engineering the immune microenvironment.
The objective of cancer therapy is therefore evolving: beyond tumor shrinkage toward deeper, more durable disease control, with treatment moving earlier in the disease course and away from monotherapy toward personalized, rational combination regimens.
👉 Within this emerging landscape, mezigdomide, gedatolisib, relacorilant, and icotrokinra collectively illustrate the breadth and direction of contemporary innovation.
- 1️⃣ Mezigdomide
Mezigdomide, a next-generation CELMoD agent, elevates molecular glue–mediated protein degradation to a new level of sophistication.
By binding to the cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase and reshaping its substrate specificity, mezigdomide labels previously “undruggable” oncogenic transcription factors—such as Ikaros and Aiolos—for proteasomal destruction.
✨ This mechanism confers two major advantages: the ability to eliminate proteins that lack conventional small-molecule binding pockets, and sustained biological activity that persists even after drug clearance, as degraded proteins require time to be resynthesized.
Mezigdomide has the potential to reshape therapeutic sequencing in multiple myeloma, particularly for patients who have exhausted lenalidomide- and pomalidomide-based regimens.
Its significance lies not only in efficacy, but in re-establishing treatment options where few remain—and potentially moving earlier in the line of therapy.
- 2️⃣ Gedatolisib
Gedatolisib exemplifies dual-pathway blockade as a strategy to overcome therapeutic escape. As a combined PI3K and mTOR inhibitor, it simultaneously suppresses two central signaling axes governing tumor growth and survival.
This design directly addresses the compensatory feedback loops commonly observed within the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway—mechanisms that frequently undermine single-node inhibition.
✨ Gedatolisib’s clinical success in HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer underscores the value of simultaneous PI3K and mTOR inhibition in overcoming endocrine resistance.
This marks an important conceptual shift: in biologically complex cancers, single-pathway suppression is often insufficient, and rational multi-target strategies may be required for durable control.
- 3️⃣ Relacorilant
Relacorilant adopts a fundamentally different approach by targeting the tumor ecosystem rather than tumor cells themselves.
As a selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, it counteracts cortisol-mediated resistance to chemotherapy.
In the tumor microenvironment, cortisol can blunt cytotoxic efficacy and promote immunosuppression; relacorilant effectively releases this molecular “brake,” restoring chemosensitivity without increasing chemotherapy dose intensity.
Relacorilant offers new hope in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, a notoriously difficult-to-treat population.
Its innovation lies in reframing combination therapy—not by intensifying cytotoxicity, but by modifying the tumor microenvironment to restore therapeutic sensitivity.
- 4️⃣ Icotrokinra
Icotrokinra represents the advance of small-molecule immunomodulation into biologic-dominated territory.
As an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist, it targets the same core inflammatory pathway as injectable anti-IL-23 monoclonal antibodies used in autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis—while offering unmatched convenience through once-daily oral dosing.
Icotrokinra may ultimately redefine treatment algorithms for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
Should its efficacy and safety profile be fully validated, a once-daily oral agent could become the preferred choice for many patients, challenging the long-standing dominance of injectable biologics as the gold standard.
🔴 Collectively, these therapies illustrate a broader industry transition—from target inhibition to protein clearance, from linear pathways to network control, and from standardized regimens to tailored combinations.
2026 Pharma Trend #4: Drug Delivery Technologies Shift from Systemic Administration to Localized, Long-Acting, and Minimally Invasive Solutions
🎯 In the traditional narrative of pharmaceutical innovation, mechanism of action has long occupied center stage, while the means by which a drug is delivered to its site of disease has often been treated as secondary.
🤔 That hierarchy is now rapidly changing. The industry increasingly recognizes that even the most potent molecule will fall short of its potential if it cannot reach the right tissue, at the right time, and at the right concentration.
Drug delivery is evolving from a supporting function into a core competitive differentiator.
From oral alternatives to injectable therapies, to extended-release formulations that lengthen dosing intervals, to localized delivery systems that maximize target-organ exposure while minimizing systemic effects, a quiet revolution is underway—one focused on optimizing the “journey” of the drug, not just its molecular design.

Nowhere is this shift more evident than in oncology, chronic disease management, and conditions requiring localized treatment, where advanced delivery systems are increasingly defining therapeutic differentiation and, in some cases, revitalizing established drugs.
👉 Within this paradigm, Johnson & Johnson’s INLEXZO (TAR-200) stands as a compelling example.
- 1️⃣ INLEXZO
The elegance of the INLEXZO system lies in its precise integration of spatial control and temporal control.
- 🧬 Spatially, the intravesical implant delivers the cytotoxic agent gemcitabine directly and continuously into the bladder lumen.
✅ This enables therapeutic drug concentrations at the bladder wall—the site of tumor recurrence—while maintaining minimal systemic exposure, thereby preserving antitumor efficacy and substantially reducing adverse effects such as myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting.
- ⌛ Temporally, its silicone-based controlled-release technology enables near-constant drug delivery over a period of up to three weeks.
✅ This creates a stable therapeutic window and avoids the “peak-and-trough” fluctuations characteristic of conventional intravesical chemotherapy, where high initial concentrations often cause irritation and toxicity, followed by subtherapeutic exposure that compromises efficacy.
Each implant can support up to 14 treatment cycles (approximately 10 months), making long-term disease management feasible within a single, minimally invasive intervention.
It is transforming the management of non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) from a model of repetitive, burdensome procedures to one of single-procedure, sustained intervention.
Historically, patients with BCG-unresponsive high-risk disease faced a stark choice:
- Frequent intravesical chemotherapy—often administered weekly over six weeks, requiring catheterization and prolonged monitoring
- Radical cystectomy, a life-altering and irreversible surgery associated with significant morbidity and quality-of-life impairment.
✨ INLEXZO introduces a third pathway.
Its five-minute outpatient implantation procedure, followed by simplified maintenance dosing every three weeks during induction and up to every twelve weeks during maintenance, dramatically reduces both physical burden and time costs for patients.
More importantly, it makes bladder preservation a realistic option for high-risk patients—a shift with profound implications for body image, urinary function, and long-term quality of life.
Taken together, these four battlegrounds and eleven spotlighted medicines form far more than a list of promising assets—they outline a structural shift in how medicines are discovered, developed, delivered, and valued.
☺️ Across metabolic disease, rare disorders, oncology/immunology, and drug delivery technologies, innovation is no longer driven by single-target potency alone, but by the ability to reshape disease biology, overcome resistance, extend durability, and meaningfully improve patients’ lived experience.
What These 11 Drugs Reveal About the Future of Pharma
When viewed individually, each of these 11 drugs represents an important clinical advance within its own therapeutic niche.
Taken together, however, they reveal something far more significant: a structural shift in how medicines are discovered, developed, delivered, and ultimately valued.
✅ Across metabolic disease, rare diseases, oncology and immunology, and drug delivery technologies, innovation in 2026 is no longer defined by whether a drug hits a target—but by whether it can redefine disease biology, overcome resistance, sustain efficacy over time, and measurably improve the lived experience of patients.
- From target inhibition to system reprogramming (The transition from simple target inhibition to active biological reprogramming)
- BGB-16673 and mezigdomide no longer aim to suppress pathological proteins—they eliminate them altogether.
- Multi-pathway agents like retatrutide move beyond single-axis metabolic control to orchestrate coordinated regulation of energy intake, expenditure, and organ-specific metabolism.
- Like relacorilant demonstrates that reshaping the tumor microenvironment can be just as powerful as directly attacking tumor cells.
- Durability becomes the new efficacy benchmark (The goal is fewer relapses, fewer interventions, and longer periods of stability)
- Ultra–long-acting biologics such as depemokimab (Exdensur)
- CNS-penetrant agents like tolebrutinib
- localized sustained-release systems such as INLEXZO (TAR-200)
- Delivery is no longer an afterthought
- Oral GLP-1 therapy (orforglipron)
- Oral IL-23 blockade (icotrokinra)
✨ The most impactful therapies of 2026 are not just products—they are platforms around which new standards of care, new clinical pathways, and new value frameworks are formed.
Conclusion: A New Definition of Pharmaceutical Leadership
Ultimately, these four innovation arenas and eleven standout drugs represent far more than a promising pipeline snapshot.
They outline a new definition of pharmaceutical leadership. In 2026, the companies that shape the future of the industry will not be those that simply launch effective drugs, but those that can:
- Reprogram disease biology rather than suppress symptoms
- Deliver durable, meaningful control instead of transient responses
- Integrate convenience, tolerability, and quality of life into efficacy
- Build scalable systems around patients, not just molecules
For stakeholders across the pharmaceutical value chain, this shift carries profound implications.
😊 Innovation no longer ends at regulatory approval—it must be translated into real-world access, continuity of care, and sustainable supply.
This is where the role of partners like DengYue becomes increasingly strategic.
As a global pharmaceutical wholesaler operating at the intersection of innovation and clinical practice, DengYue’s mission is not merely to move products, but to enable therapies to reach the right patients, at the right time, through the right channels.
Whether supporting the distribution of ultra–long-acting biologics, complex drug–device combinations, or next-generation oral therapies, the ability to align logistics, compliance, and clinical value is becoming a core pillar of modern pharma leadership.
In that sense, the question is no longer which drugs will succeed. The real question—and the one these 11 drugs begin to answer—is which vision of medicine will define the next decade of pharma innovation.
FAQ about Which 11 Drugs Will Define the Future of Pharma
What is the pharmaceutical trend in 2026?
Innovative Technologies
What drugs will be lower in 2026?
The 5 drugs with negotiated lower prices for 2026:
1. Eliquis for blood clot prevention and treatment
2. Enbrel for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
3. Entresto for heart failure
4. Farxiga for diabetes, heart failure and chronic kidney disease
5. Fiasp and NovoLog, types of insulin for diabetes
What is the new weight loss drug in 2026?
Starting Jan. 5, 2026, pharmacies across the country began stocking the Wegovy tablets.
What are they replacing Ozempic with?
For Type 2 diabetes, this may include Rybelsus, Trulicity, or Mounjaro. If you’re taking Ozempic off-label for weight loss, Wegovy, Zepbound, and Saxenda are three FDA-approved options.