Abbisko’s Pimicotinib (ABSK021) for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor: China’s First Class-1 CSF-1R Inhibitor Approved for TGCT
In the field of tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT), a rare but persistent disease that impairs joint function, long-term systemic treatment options are limited.
The emergence of Pimicotinib (ABSK021), a highly selective CSF-1R inhibitor developed in China, is beginning to change this landscape. Developed by Abbisko, this drug was approved in China in 2025 for TGCT.
Pimicotinib (ABSK021) for tenosynovial giant cell tumor is the first Class 1 chemical innovative drug approved in China for TGCT, making China one of the major markets to achieve regulatory approval and clinical accessibility for this therapy.

Simultaneously, Pimicotinib has entered into a global commercialization collaboration with Merck, encompassing $85 million in option payments, up to approximately $605.5 million in milestone payments, and future sales revenue sharing, marking a significant step for Chinese innovative drugs into the global market.
As innovative therapies accelerate into global collaborative development and supply networks, DengYueMed continues to explore efficient and compliant pathways to bring breakthrough drugs to patients worldwide.
Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor (TGCT): Disease Characteristics and Long-term Unmet Needs
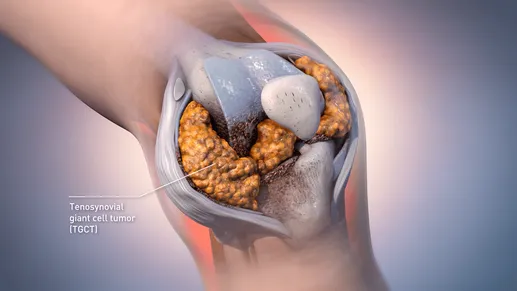
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is a rare, locally invasive benign tumor originating from the synovium, bursae, and tendon sheath tissue of joints.
👉 Based on different growth patterns, it is generally divided into two main subtypes: localized (L-TGCT) and diffuse (D-TGCT), with the diffuse type being more aggressive and associated with a higher risk of recurrence.
From an epidemiological perspective, TGCT is a rare disease globally, reported in populations in Europe, North America, and East Asia. Current research indicates:
- Localized TGCT has an incidence of approximately 10–50 cases per million people.
- Diffuse TGCT has an incidence of approximately 5–10 cases per million people.
- The age of onset is concentrated in young and middle-aged adults aged 35–50.
- The gender distribution is generally similar, but some cohort studies suggest a slight increase in females.
While TGCT rarely poses a direct threat to life, persistent synovial hyperplasia and inflammation can cause joint swelling, chronic pain, and limited mobility, leading to long-term impairment of quality of life.
Surgical resection remains the first-line treatment; however, diffuse lesions are difficult to completely remove, with a recurrence rate of approximately 20%–50%. Repeated surgeries may even lead to joint replacement or amputation, resulting in a persistent gap in systemic treatment.
🎇 Molecular studies have shown that most cases of TGCT involve CSF1 rearrangement and activation of the CSF-1R pathway, driving disease development. Therefore, blocking this signaling axis is a key therapeutic approach.
Although pexidartinib has been approved in the US, its hepatotoxicity limits its effectiveness, and a new generation of safer, more selective long-term treatment remains urgently needed.
China’s Innovation: Pimicotinib Mechanism of Action and Key Clinical Evidence
It is against this backdrop of unmet needs that Pimicotinib (ABSK021), independently developed by a Chinese company, entered clinical trials and achieved a key breakthrough.
This drug is an oral, highly selective, small-molecule CSF-1R inhibitor:
- Its molecular design aims to: precisely inhibit the pathogenic target
- Reduce off-target toxicities
- Provide a safety window more suitable for long-term treatment
MANEUVER: A Phase III Study of Pimicotinib in TGCT
The approval of Pimicotinib is primarily based on the global, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III MANEUVER study, which systematically evaluated its efficacy and safety in patients with inoperable or symptomatic TGCT.
The study showed that at week 25, the objective response rate (ORR) in the Pimicotinib group reached 54.0%, while it was only 3.2% in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001).
✅ Simultaneously, patients also experienced consistent improvements in joint function, pain, and overall symptoms, confirming the clinical significance of the efficacy and providing a new treatment option for TGCT, which has long lacked effective systemic therapy.
Sustained Efficacy and Symptom Benefit of Pimicotinib in TGCT
Long-term follow-up results further solidified the therapeutic value of Pimicotinib in TGCT.
👏 At a median follow-up time of 14.3 months, the ORR in the study population increased to 76.2%, with some patients achieving complete remission, suggesting that the drug not only rapidly induces tumor shrinkage but also possesses sustained and stable anti-tumor activity.
In addition to tumor shrinkage, joint range of motion, pain and stiffness, and patient-reported physical function all showed significant improvements, suggesting that CSF-1R inhibition can simultaneously provide structural control and functional benefits.
Safety and Tolerability of Pimicotinib in TGCT
Compared with previous studies of CSF-1R inhibitors, Pimicotinib (ABSK021) for tenosynovial giant cell tumor shows a potential trend toward improved safety.
Current data show a low rate of ≥ grade 3 adverse events and dose reductions or discontinuations due to adverse reactions, and no drug-related liver injury or cholestatic hepatotoxicity signals were observed, nor were there significant pigment changes or other toxicities affecting long-term adherence.
✨ These characteristics suggest that it may be more suitable for long-term disease management in TGCT while maintaining efficacy.
Commercialization Progress and Global Market Significance of Merck KGaA Pimicotinib
From a global industry collaboration perspective, Pimicotinib has entered into an exclusive licensing agreement with Merck KGaA to promote its development and commercialization outside of Greater China.
This is considered by the industry as a landmark event in the “going global” of innovative Chinese oncology drugs.

For rare but potentially disabling diseases like TGCT, the core value of drug commercialization lies not only in sales volume, but more directly in three aspects: patient accessibility, global coverage potential, and long-term treatment attributes:
1️⃣ China Achieves Standardized Access First
The official approval of pimicotinib (ABSK021) for tenosynovial giant cell tumor in China transforms TGCT systemic therapy from “limited options” to “realistically available,” marking a new stage in China’s accessibility to targeted therapy for rare tumors.
It also positions the country as one of the most clearly defined major markets for TGCT targeted therapy globally.
2️⃣ A Global Commercial Path is Taking Shape
Collaborations with multinational pharmaceutical companies lay the foundation for subsequent international registration and market entry, meaning that the scope of patient benefits is expected to gradually expand from a single country to a wider range of regions.
As original Chinese targeted drugs go global, DengYueMed provides compliant cross-border supply and professional distribution services, driving innovative therapies to reach real patients in different regions more efficiently.
3️⃣ Long-Term Treatment Attributes Determine Real Market Demand
TGCT typically requires long-term disease control rather than short-term cure. Therefore, the sustained efficacy, safety, and adherence of the drug directly determine its real clinical value and market stability.
Conclusion
The advancement of pimicotinib (ABSK021) for tenosynovial giant cell tumor demonstrates that Chinese pharmaceutical innovation is shifting from following to original breakthroughs, providing a new global solution in the field of targeted therapy for rare diseases.
From an industry perspective, its advancement also signifies that the company is moving from R&D to the commercialization stage, with collaborative returns and financial support laying the foundation for subsequent pipeline development.
In the process of making innovative therapies globally accessible, global pharmaceutical distributor Dengyue Medicine is becoming a crucial link connecting scientific research results with real patients.
FAQ about Pimicotinib (ABSK021) for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor
Is pimicotinib approved as systemic treatment in China for Tenosynovial giant cell tumor?
China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approved pimicotinib (ABSK-021) as the first domestically developed systemic therapy for tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) in December 2025.
What is the route of administration for pimicotinib?
Pimicotinib is administered orally as a small-molecule CSF-1R inhibitor.
What is the mechanism of action of ABSK021?
ABSK021 (pimicotinib) is an orally available, highly selective small-molecule CSF-1R inhibitor that blocks CSF-1R signaling and modulates macrophage activity, thereby suppressing inflammation-driven tumor growth and disease progression.
Is TGCT a rare condition?
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is considered a rare disease, with reported incidence generally ranging from approximately 10 to 50 cases per million people, depending on subtype and population.