
Glumetinib Approval in China: A Major Breakthrough for MET-Positive Lung Cancer
On March 8, 2023, China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) announced a significant glumetinib approval—the conditional market authorization of the Class 1 innovative drug Glumetinib Tablets (brand name: Hai Yi Tan®), developed by Shanghai HaiHe Pharmaceutical.
This decision not only represents another major breakthrough in China’s lung cancer targeted therapy field but also signifies that thousands of patients with a specific type of lung cancer have gained a new treatment option.
As an important partner for the subsequent commercialization of this drug, Hong Kong DengYue Medicine will help make it accessible to more patients in China.
Data shows that MET gene abnormalities account for approximately 3-4% of non-small cell lung cancer cases, among which MET exon 14 skipping mutation–positive NSCLC is one of the most clinically significant subtypes.
👉 Prior to the approval of glumetinib, these patients often faced limited and ineffective treatment options.
Today, let us delve into how this innovative drug is transforming the treatment landscape for specific lung cancer patients.
Weapon Design—Key Insights into the Molecular Structure and Mechanism of Action of Glumetinib
If lung cancer cells are like machines that have spiraled out of control due to genetic mutations, then glumetinib is a precision-engineered brake designed specifically for them.
To understand why it is so effective, we must step into its molecular world.
Drug Profile: A Highly Specific “Molecular Key”
First, it’s essential to define the identity of glumetinib. It is an oral, potent, and highly selective small-molecule MET inhibitor. These three attributes are indispensable:
- 🥛 Oral: Determines convenience of administration, enabling at-home treatment and significantly improving patients’ quality of life.
- 💪 Potent: Means it not only binds to the target but does so with sufficient strength to produce robust inhibition even at low concentrations, ensuring efficacy in the complex human biological environment.
- 🙂 Highly Selective: This is the core of its safety and precision. It acts almost exclusively on the MET target, akin to a key that fits only one lock, minimizing damage to normal cellular functions and thereby substantially reducing off-target side effects.
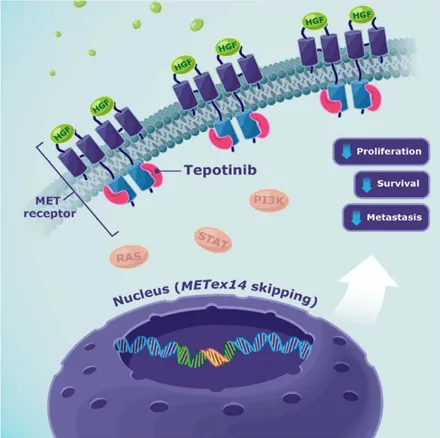
Mechanism of Action: Precision Targeting, Shutting Down the Cancer Cell’s “Command Center”
The MET receptor tyrosine kinase (mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor), short for “Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor,” functions like a “signal antenna” and “command switch” on the cell membrane.
Normally, it briefly activates upon receiving specific growth factor signals, directing normal cellular growth and repair.
👉 However, in cancer cells harboring the MET exon 14 skipping mutation, this switch is permanently stuck in the “ON” position due to the loss of a key regulatory domain, relentlessly transmitting growth signals.
Glumetinib’s role is to directly correct this fatal switch malfunction. The process can be broken down into two precise steps:
1️⃣ Precision Locking (Target Binding)
The molecular structure of glumetinib is meticulously designed and optimized to function like a custom-made key, accurately inserting into and occupying the core functional region of the MET kinase—the ATP-binding pocket.
This is the “chemical ignition switch” for signal transduction, requiring binding with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to activate.
Through superior binding affinity, glumetinib competitively occupies this site, physically blocking ATP binding and preventing the MET receptor tyrosine kinase from being phosphorylated and activated.
In essence, its sophisticated molecular conformation jams the start button of this faulty switch.
2️⃣ Effective Inhibition of Downstream Oncogenic Signaling (Signal Blockade)
Once the MET “effective inhibition of downstream oncogenic signaling” within the cell is successfully suppressed, the entire downstream oncogenic signaling network is paralyzed.
The two most critical pathways—the cancer cell’s lifelines—include:
- The RAS-MAPK Pathway: Primarily responsible for transmitting “proliferate and divide” commands.
Blocking this pathway cuts off the core instruction for cancer cells to replicate themselves.
- The PI3K-AKT Pathway: Primarily responsible for transmitting “survive and resist death” commands and regulating cellular metabolism.
Inhibiting this pathway significantly weakens the cancer cell’s ability to resist programmed cell death and maintain high-energy metabolism.
Simultaneously, other signals related to cancer cell invasion, migration, and angiogenesis (such as STAT3, FAK) are also suppressed.
Through this multi-pronged approach, cancer cells are not only forced into “dormancy” but also pushed toward apoptosis, fundamentally curbing tumor growth and spread.
Unique Structure Yields Three Major Pharmacological Advantages
The exceptional characteristics demonstrated by glumetinib in preclinical and clinical studies are not accidental but the inevitable result of its ingeniously designed molecular structure.
This is primarily reflected in three core pharmacological advantages:
1. High Selectivity: Rooted in Atomic-Level Precision Matching
Specific groups on its chemical scaffold can form multiple, high-strength intermolecular forces with amino acid residues within the MET kinase’s ATP-binding pocket, including precise hydrogen-bond networks, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions.
🔐 This “lock-and-key complementarity” at the atomic level gives glumetinib nanomolar-level affinity for the MET target while having minimal activity impact on other structurally similar kinases (such as AXL, VEGFR2, KDR).
This exceptionally high selectivity directly translates into low off-target toxicity in the clinic, meaning powerful tumor inhibition comes with a significantly reduced risk of damage to normal tissues like the heart and blood vessels.
2. Pharmacokinetic Advantage: “Long-Acting Stability” Engineered by Design
- Long Half-life (~40-50 hours): Thanks to its stable chemical structure and low affinity for metabolic enzymes, glumetinib is cleared slowly from the human body.
✅ This allows for once-daily oral administration to maintain stable blood concentrations throughout the day, greatly simplifying the treatment regimen and enhancing patient compliance.
- High and Sustained Steady-State Plasma Concentration: With optimized dosing, glumetinib rapidly achieves and maintains blood concentrations well above its half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) after continuous administration.
✅ This ensures “continuous, deep inhibition” of the MET target throughout the 24-hour dosing interval, denying cancer cells any potential window for recovery or adaptation, theoretically delaying the onset of resistance.
3. Potent Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration: The Foundation for Conquering the Treatment “Sanctuary”
Brain metastases in lung cancer are a major cause of treatment failure and mortality.
The challenge lies in the fact that most drug molecules cannot effectively cross the protective blood-brain barrier due to their size, polarity, or charge.
Glumetinib’s moderate molecular weight, optimal lipid-water partition coefficient, and low P-glycoprotein substrate properties—all carefully optimized physicochemical traits—give it exceptional central nervous system penetration.
Preclinical models show a significantly higher brain-to-plasma concentration ratio compared to earlier-generation MET inhibitors.
This provides a solid material basis for its high efficacy against brain metastases in the real world, enabling comprehensive anti-cancer coverage from the peripheral circulation to the central nervous system.
Thus, the success of glumetinib is no accident.
✨ From the precision of its highly selective binding to the long-acting stability of its pharmacokinetics and the exceptional ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, each of its advantages is deeply rooted in its original rational drug design philosophy.
This meticulously forged “molecular key” possesses, in theory, all the essential elements of a transformative drug.
However, even the most elegant theoretical design must be tested on the complex battlefield of the real world.
So, how does this “custom-made key” perform when unlocking hope for patients’ lives? Have these molecular-level advantages truly translated into measurable, tangible clinical benefits?
Let’s now proceed to Part II, where we will examine the solid evidence from clinical trials that validates this remarkable journey from “molecular blueprint” to “life-saving reality,” further underscoring the importance of its recent glumetinib approval in advancing lung cancer targeted therapy. 🔻
The Trial by Fire—How Key Clinical Data Validate Its Design Superiority
If laboratory data paint an ideal blueprint, then clinical studies are the engineering that turns that blueprint into reality.
The global Phase II GLORY study was glumetinib’s “trial by fire”—not only validating its exceptional efficacy but also perfectly aligning with every aspect of its ingenious design, providing crucial supporting evidence for the glumetinib approval process.
Data Overview: An Encouraging Report Card
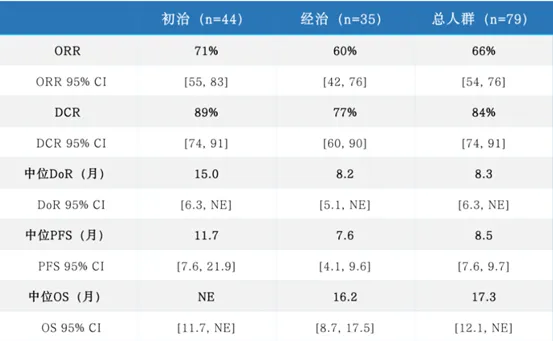
In patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring MET ex14 skipping mutations, glumetinib delivered exceptional results, further solidifying its important position among lung cancer targeted therapy drugs:
- Objective Response Rate (ORR): High Response Rates Highlight Potent Nature
As assessed by a blinded independent review committee, the overall ORR reached 66%, meaning tumors shrank by more than 30% in two-thirds of patients. Notably:
- Treatment-naïve patients achieved an impressive ORR of 71%, suggesting significant potential as a first-line therapy.
- Previously treated patients also had an ORR of 60%, offering new hope for later lines of therapy.
This data surpasses the performance of many previous non small cell lung cancer targeted therapy drugs in similar patient populations, fully validating its potent inhibitory capabilities.
- Depth and Duration of Response: Evidence of Sustained Benefit
- Median Duration of Response (DoR): 8.3 months in the overall population, with treatment-naïve patients achieving an excellent 15.0 months.
- Rapid Onset of Action: Median time to response was only 1.4 months, with most patients showing improvement at the first assessment.
- Progression-Free Survival (PFS): Extending Disease Control
- Median Progression-Free Survival: 8.5 months in the overall population.
- Extended to 11.7 months in treatment-naïve patients, granting patients over a year of quality survival time.
- Efficacy in Brain Metastases: A Breakthrough in Treatment
The most striking highlight is its efficacy in patients with brain metastases:
- Baseline brain metastasis patients achieved an ORR as high as 85%, a breakthrough figure.
- All 5 measurable brain target lesions showed shrinkage, confirming its intracranial activity.
This finding is highly significant, as brain metastases have been a major challenge in the development of non small cell lung cancer drug.
Perfect Alignment of Mechanism and Data: A Victory for Design Philosophy
The GLORY study results are no accident but the inevitable outcome of glumetinib’s thoughtful design. This clinical data forms a perfect closed loop with its glumetinib mechanism of action:
1. High Response Rates ↔ Clinical Manifestation of Potent Inhibition
The 66%-71% high ORR directly validates glumetinib’s nature as a “potent” inhibitor. This data indicates that it not only binds to the MET target but also produces inhibition strong enough to quickly suppress the MET-driven signals in most patients. This is direct clinical evidence that its molecule can powerfully occupy the ATP pocket and efficiently block downstream pathways.
2. High Efficacy in Brain Metastases ↔ Empirical Proof of Exceptional BBB Penetration
The 85% response rate in brain metastases provides the strongest clinical evidence, confirming a key advantage in the drug’s design—exceptional central nervous system penetration. This data shows:
- Glumetinib can not only theoretically cross the blood-brain barrier but also reach effective therapeutic concentrations in actual patients.
- It addresses the long-standing challenge in traditional non small cell lung cancer new treatment of penetrating the CNS.
- It offers a truly effective new drug for non small cell lung cancer option for patients with brain metastases.
3. Durable Efficacy ↔ Translation of Pharmacokinetic Advantages
The up to 15-month duration of response observed in treatment-naïve patients directly reflects its pharmacokinetic advantages, including a long half-life and high steady-state plasma concentrations. This “long-acting stability” means:
- Drug concentrations remain continuously above the effective threshold, enabling 24/7 inhibition.
- It delays disease progression, granting patients longer periods of quality survival.
- It reduces the chance of resistance development, extending the treatment benefit period.
Safety Data: The Clinical Benefit of High Selectivity
Glumetinib demonstrates an overall favorable safety profile. The most commonly reported adverse reactions include peripheral edema, nausea, and elevated liver function tests, most of which are Grade 1-2 in severity and can be managed through supportive care or dose adjustments.
This relatively manageable side-effect profile is a direct clinical reflection of its high selectivity.
By specifically targeting the MET kinase with precision, glumetinib avoids the severe off-target toxicities—such as hypertension, bleeding events, and cutaneous toxicities—that are often associated with the broad inhibition of multiple kinases.
Consequently, patients can receive long-term treatment with improved tolerability, supporting sustained therapeutic benefits.
👉 TBased on robust clinical data, the GLORY study demonstrates clinically relevant outcomes that are consistent with glumetinib’s molecular design and pharmacological properties.
This is not only a confirmation of scientific hypotheses but also a success story in translational medicine—transforming a molecular blueprint from the laboratory into fruitful clinical research outcomes, and ultimately into tangible survival benefits for patients.
The Path Forward – The Potential, Challenges, and Boundless Possibilities for Glumetinib
The successful market entry of glumetinib is not the end of the story, but rather the beginning of a broader chapter.
As an innovative drug with outstanding clinical potential, its future development is advancing along three clear and critical trajectories, building upon the foundation laid by its recent glumetinib approval.
Trajectory One: Deepening and Expanding – Pursuing Excellence in the Core Battlefield
1. Confirmatory Phase III Studies Underway
The current “conditional approval” is based on the excellent data from the Phase II GLORY study.
To obtain full approval and provide the highest level of evidence for clinical practice, glumetinib is undergoing or planning large-scale, randomized, controlled Phase III clinical trials. These studies aim to:
- Head-to-Head Validation of Advantages: Directly compare glumetinib with existing standard treatments (such as chemotherapy) to further confirm its superiority in terms of PFS, OS (overall survival), and other endpoints.
- Establishing the Gold Standard for First-Line Treatment: The GLORY study suggested that treatment-naïve patients benefit more significantly. Future research will clarify its position in first-line therapy, potentially providing a new preferred treatment regimen for patients with MET ex14 skipping mutations.
2. Addressing the Challenge of Resistance – Exploring Next-Generation Solutions
As with all targeted therapies, resistance is an inevitable scientific challenge. The core focus of future research will be to explore:
- What Are the Resistance Mechanisms? Are they secondary mutations in the MET gene (such as D1228N, Y1230C, etc.), or the activation of other bypass signaling pathways (such as EGFR, HER3)?
- How Can Resistance Be Overcome? Developing next-generation MET inhibitors targeting specific resistance mutations or exploring combination therapy regimens of glumetinib with drugs targeting bypass activations will be key to maintaining long-term efficacy.
Trajectory Two: Boundary Exploration – Potential Beyond the Current Indication
1. Expanding MET Abnormality Types
Beyond MET ex14 skipping mutations, other MET signaling abnormalities are also important therapeutic targets:
- MET Amplification: Common in various solid tumors such as non-small cell lung cancer and gastric cancer, and a significant cause of resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies. The efficacy of glumetinib in MET-amplified populations is being actively explored.
- MET proto-oncogene product tyrosine kinase (mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor) Overexpression: Also associated with poor prognosis. Its value as a biomarker and its response to glumetinib treatment represent another dimension of research.
2. Advancing into Other Cancer Types
MET signaling abnormalities are pan-cancer. The potential of glumetinib may extend to:
- Other Lung Cancer Subtypes: Such as pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (with a high MET mutation rate).
- Digestive System Tumors: Gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, etc.
- Other Solid Tumors: Such as renal cell carcinoma, glioblastoma, etc. Clinical studies targeting these cancer types are exploring its potential as a “broad-spectrum” MET inhibitor.
Trajectory Three: Strategic Layout – Combination Therapies and a Global Vision
1. Building a New Paradigm for Combination Therapy
While monotherapy efficacy is foundational, combination therapy is often the path to greater breakthroughs and extended survival. Highly promising exploratory directions include:
- Combination with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 Antibodies): The rationale is that MET signaling inhibition may improve the tumor immune microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy efficacy. This could potentially overcome the challenge of immunotherapy insensitivity in some lung cancer patients.
- Combination with Other Targeted Therapies: For example, combining with EGFR inhibitors for upfront (first-line) treatment of EGFR/MET co-mutant lung cancer or to reverse acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs.
- Combination with Chemotherapy or Anti-Angiogenic Drugs: Exploring synergistic effects.
2. Progressing Toward a Truly Global Drug
- FDA Orphan Drug Designation Is Just the Beginning: Obtaining orphan drug designation from the U.S. FDA has accelerated its global development process. Currently, key international multicenter clinical studies are underway, aiming to accumulate data that meet international standards.
- Goal: Approval in the U.S. and Other Major Global Markets: This would not only benefit patients worldwide but also signify that China’s domestically developed innovative drugs have gained genuine recognition from global regulatory systems and the medical community, representing a “global roadshow” of China’s pharmaceutical innovation capabilities.
Conclusion
The story of Glumetinib is a condensed history of modern oncology breakthroughs. It perfectly demonstrates the complete cycle from fundamental scientific discovery to the realization of clinical value, illuminating a new beacon of hope for patients with MET exon 14 skipping mutation non-small cell lung cancer in China and globally.
Behind this success story lies not only scientific breakthroughs in research and development but also the collaborative efforts of industry partners, including the
International Drug Supplier— Dengyue Medicine in enhancing drug accessibility and market promotion.
- 😷 For Patients: It signifies a transition from “hopelessness” to “hope,” from “helplessness” to “precision counterattack.” It provides a powerful weapon, particularly for patients with brain metastases, significantly improving their quality of life and prognosis.
- 🙂 For the Chinese Pharmaceutical Industry: It stands as a milestone for “Made in China” original innovative drugs, demonstrating China’s full-chain innovation capabilities—from new target discovery and molecular design to clinical development and regulatory approval—thereby greatly boosting industry confidence.
- 🌐 For the Global Fight Against Cancer: It contributes a successful MET inhibitor model. Its data and experiences enrich the global oncology knowledge base and provide a replicable R&D paradigm for treating patients with similar rare mutations.
✨ The success of Glumetinib is a vivid practice of the precision medicine concept: identifying specific molecular abnormalities that drive disease and tailoring therapeutic weapons accordingly.
It tells us that cancer treatment is transitioning from the “one-size-fits-all” chemotherapy era to the “tailor-made” precision era.
FAQ about Glumetinib Approval
What is the mechanism of action of glumetinib?
The mechanism of action for Glumetinib centers around its ability to inhibit the MET receptor.
Is glumetinib approved by the FDA?
26 Jan, 2022, Shanghai, China—Shanghai Haihe Biopharma Co., Ltd announced that Glumetinib (SCC244) has been granted Orphan Drug Designation in the US by the Food and Drug Administration.
What is the new treatment for NF1 in 2025?
Koselugo (Selumetinib)
How close are we to curing genetic diseases?
Thus, genetic therapy is expected to lead to a cure for most monogenic disorders.
According to most of our respondents, a cure for rare genetic diseases via genetic therapies is not likely to occur in less than 15 years.



