Akeega (Niraparib Abiraterone) – mCRPC | HongKong DengYue Medicine
- Generic Name/Brand Name: Niraparib Abiraterone / Akeega®
- Indications: mCRPC
- Dosage Form: Tablet
- Specification: 100 mg, 500 mg × 60 tablets/box
Niraparib Abiraterone Application Scope
Indication: Adult patients with BRCA-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), in combination with prednisone/prednisolone.
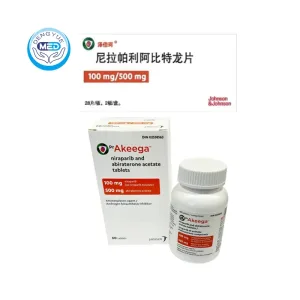
Niraparib Abiraterone Characteristics
-
Ingredients: Each film-coated tablet contains niraparib 100 mg + abiraterone acetate 500 mg.
-
Properties:
-
PARP inhibitor (niraparib) + androgen biosynthesis inhibitor (abiraterone).
-
Yellow, film-coated, oral tablets.
-
-
Packaging Specification: Bottles or blister packs; commonly 60 tablets/bottle (market-dependent).
-
Storage:
-
Store at 20–25 °C (68–77 °F); excursions 15–30 °C.
-
Keep in original container, protect from moisture and light.
-
-
Expiry Date: As printed on the package (market-dependent shelf life).
-
Executive Standard: In-house/marketed product standard (varies by market).
-
Approval Number: Market-specific registration number (fill per local label).
-
Date of Revision: Per local label (e.g., latest revision year/month).
-
Manufacturer: Janssen-Cilag / Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine (market entity varies).
Guidelines for the Use of Akeega
-
Dosage and Administration:
-
Recommended Dose: 2 tablets once daily (total niraparib 100 mg + abiraterone acetate 1000 mg).
-
Administration:
-
Oral, on an empty stomach (no food for ≥2 h before and ≥1 h after).
-
Swallow tablets whole.
-
-
Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the usual time. Do not double up.
-
-
Adverse Reactions:
-
Common Adverse Reactions: Fatigue/asthenia, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, anemia, thrombocytopenia, constipation, diarrhea, back pain, hypokalemia, edema, cough, elevated liver enzymes.
-
Serious Adverse Reactions: Myelosuppression (severe thrombocytopenia/anemia), MDS/AML (rare), hepatotoxicity, adrenal insufficiency, severe hypertension, cardiac events (rare), serious infections.
-
-
Contraindications:
-
Pregnancy (embryo-fetal toxicity).
-
Known hypersensitivity to components.
-
Severe hepatic impairment for abiraterone component (use not recommended).
-
-
Precautions:
-
Monitor CBC (platelets, hemoglobin, neutrophils).
-
Monitor BP, serum potassium, and liver function (ALT/AST, bilirubin).
-
Risk of mineralocorticoid excess (hypertension, hypokalemia, edema) — prednisone/prednisolone required.
-
Avoid grapefruit/Seville orange (CYP3A interactions).
-
Embryo-fetal toxicity: use effective contraception for partners.
-
Dose modifications/interruption for hematologic or hepatic toxicity per label.
-
Niraparib Abiraterone Interactions
-
Strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort) ↓ abiraterone exposure — avoid.
-
Strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) ↑ abiraterone exposure — avoid/monitor.
-
Abiraterone inhibits CYP2D6 and CYP2C8 → ↑ levels of substrates (e.g., metoprolol, propafenone, tricyclics) — monitor/adjust.
-
Niraparib is a substrate of P-gp/BCRP; strong inhibitors may ↑ exposure — monitor for toxicity.
-
QT-prolonging or myelosuppressive agents: additive effects — use caution.
-
Mineralocorticoid effects may be exacerbated by potassium-wasting diuretics — monitor K⁺ and BP.
Note:
- If there is a new packaging for the drug, the new packaging shall prevail. The above information is sourced from DengYue Medicine.
- This content is for reference only. Prescription drugs must be used under a doctor’s guidance and purchased from authorized sources.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.